Baebies Receives FDA Breakthrough Device Designation for First Point-of-Care Heparin Monitoring Test

A Digital Microfluidic Sepsis Diagnostic Predicts Bacterial Infection Status Using Host Transcription Response

Novel Fluorometric Assay for Pediatric Anti-Factor Xa Testing: Minimizing Bilirubin and Hemolysis Interference in Whole Blood

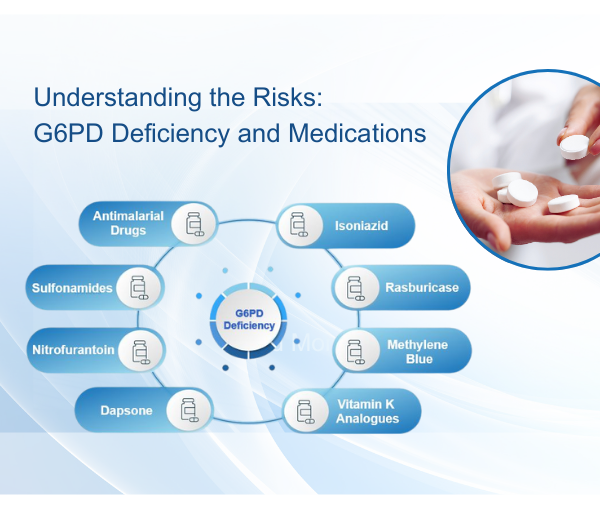
Investigation into the Prevalence of G6PD Deficiency in a Pediatric African American Population Using A Near-Patient Diagnostic Platform

Digital Microfluidic Point of Care Platform for Molecular Detection of STI Pathogens Including Drug-Resistant Gonorrhea

A Digital Microfluidic Sepsis Diagnostic Predicts Bacterial Infection Status Using Host Transcriptomic Response

Preliminary Clinical Method Comparison of a Point-of-Care Platform for anti-Factor Xa in Pediatric Patients on Heparin Therapy

Baebies Awarded $2.7 Million NIH Grant for Rapid, Near-patient Heparin Monitoring Requiring Low Sample Volume

Baebies Awarded up to $11.6 Million from CARB-X for the Development of a Diagnostic Platform with Rapid Results for Sepsis